
Press Releases
29.04.2025
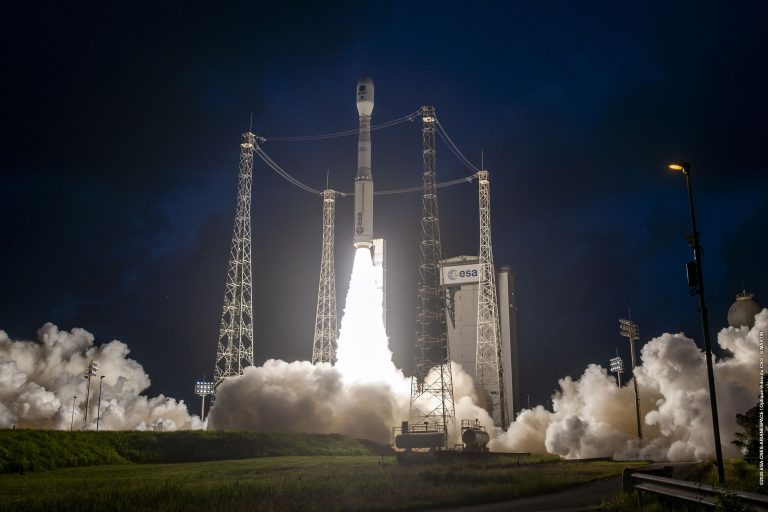
Arianespace Successfully Launches Esa’s Biomass Satellite
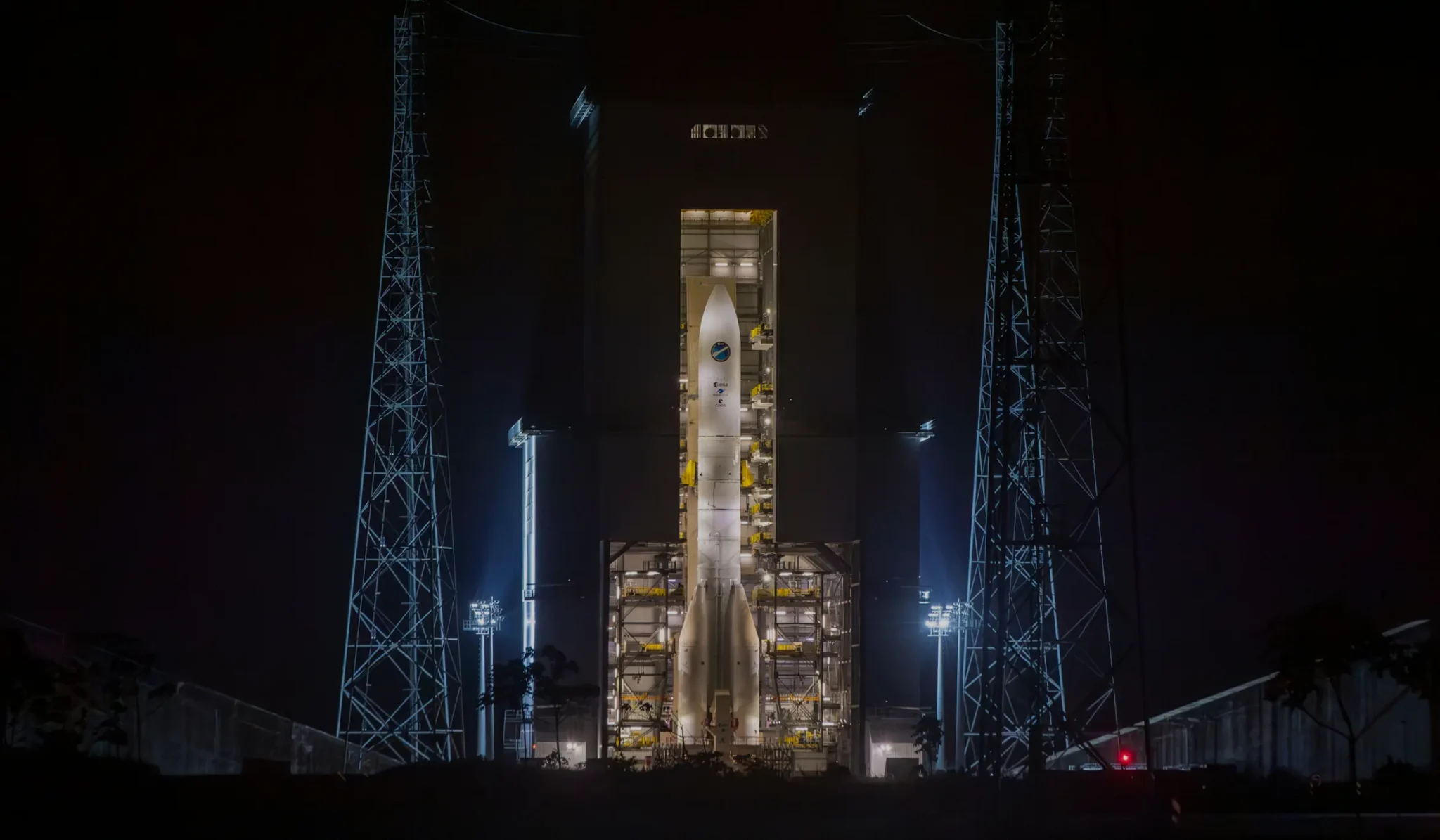

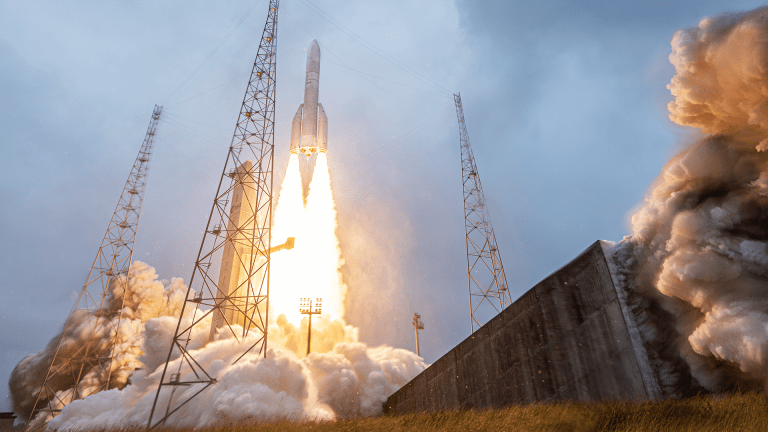
Flight VA263 - CSO-3

Press Releases
17.06.2025
Arianespace to launch CO3D and MicroCarb satellites on July 25, 2025, with Vega C

Press Releases
29.04.2025
Arianespace Successfully Launches Esa’s Biomass Satellite

Press Releases
28.04.2025
Olivier Ricouart appointed Chief Technical Officer of Arianespace

Press Releases
25.03.2025
Arianespace to launch ESA’s Biomass satellite on April 29, 2025, with Vega C

Press Releases
10.03.2025
Arianespace announces the retirement of Wiener Kernisan; Amer Khouri named president of Arianespace, Inc.
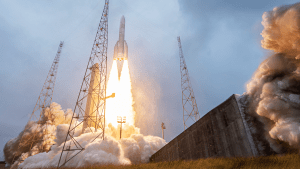
Ariane 6
07.03.2025
Flight VA263 - CSO-3

Press Releases
06.03.2025
Ariane 6 performs first commercial flight with successful launch of CSO-3 satellite

Press Releases
05.03.2025
Flight VA263 now scheduled on March 6, 2025

Press Releases
03.03.2025
Flight VA263: Postponement of the launch

Press Releases
25.02.2025
Flight VA263 now scheduled on March 3, 2025

Press Releases
21.02.2025
Flight VA263: New launch date to be confirmed soon

Press Releases
29.01.2025
Arianespace to launch ESA's space telescope PLATO with Ariane 6

Press Releases
28.01.2025
Arianespace signs Ariane 6 launch contract for Galileo’s first pair of second-generation satellites

Press Releases
28.01.2025
The European Commission, ESA, and EUMETSAT sign two agreements with Arianespace on Ariane 6

Ariane 6
15.01.2025
The CSO-3 satellite has arrived at Europe's Spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana

Corporate
19.12.2024
ArianeGroup and Arianespace announce the departure of Stephane Israël, CEO of Arianespace, and the appointment of his successor David Cavaillolès