Tailor-made launch solutions from Arianespace for all missions and orbits
For more than 40 years, Arianespace has supported its commercial and institutional customers through its range of launchers capable of placing satellites in orbit for all types of space missions, such as telecommunications, navigation, Earth observation, science, technological demonstrations.

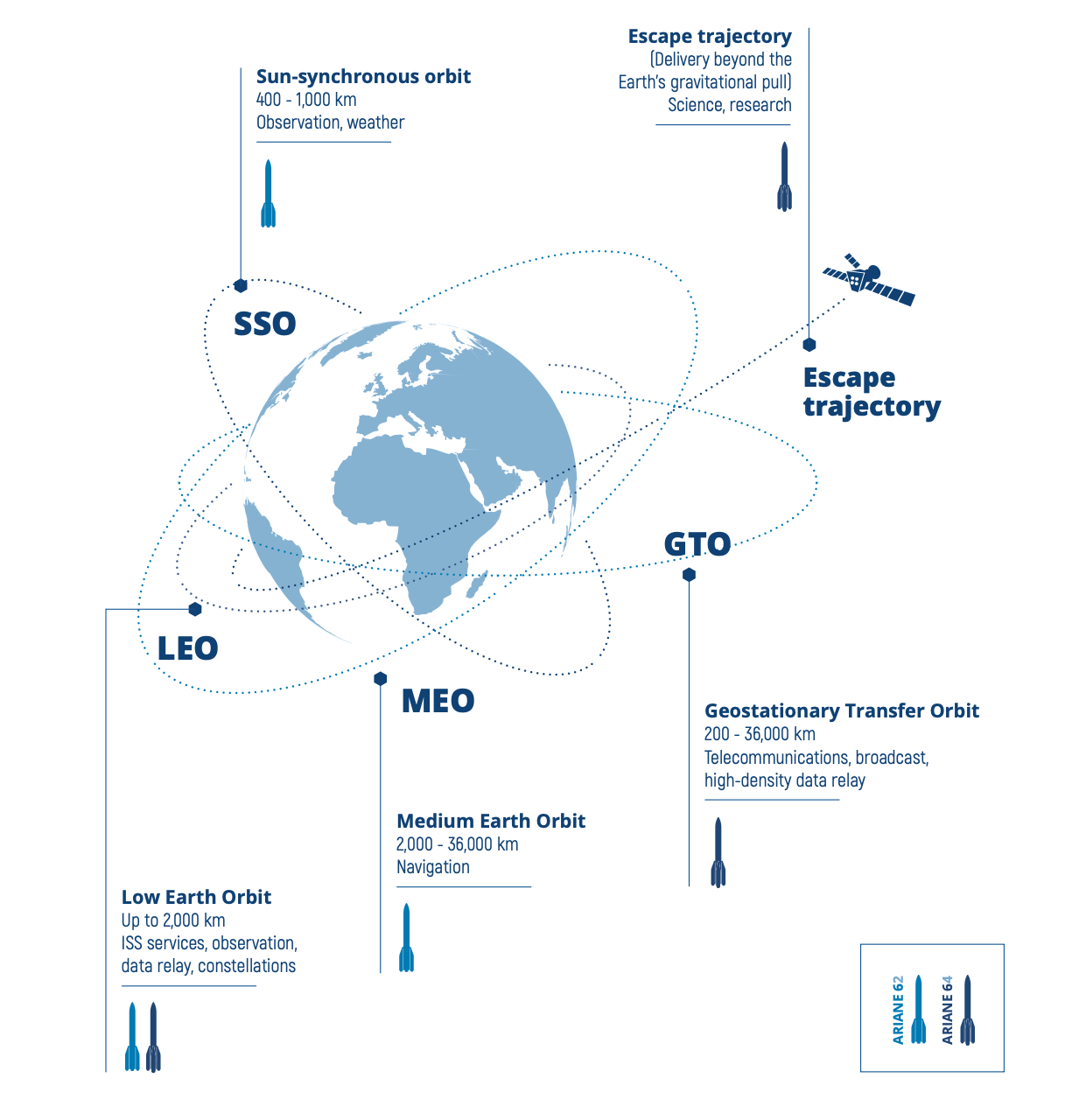
Our launch solutions are tailored to each individual objective. Whether the satellites are placed:
In low Earth orbit (LEO) for Earth observation,
In medium Earth orbit (MEO) for navigation,
In geostationary orbit (GTO) for telecommunications,
Or on separation trajectories for scientific and exploration missions.
Our solutions are designed to maximize performance and precision while minimizing costs and environmental impact.
See how our launchers guarantee Europe’s sovereignty, with solutions for every orbit.
Examples of missions
-
OneWeb low-Earth orbit satellite constellation (LEO)
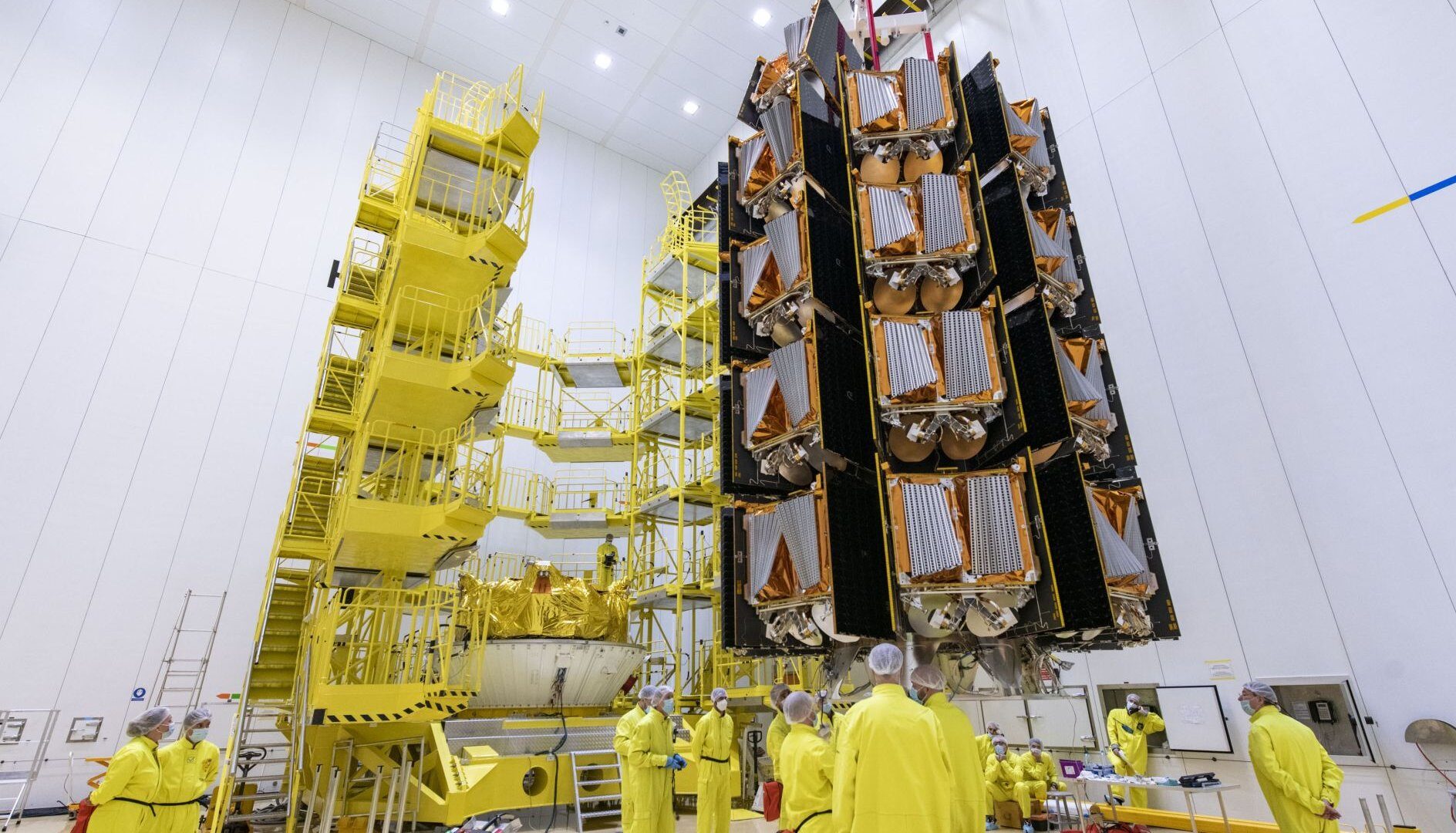

OneWeb aims to provide global Internet connectivity via a constellation of satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO). Over three years, Arianespace carried out 13 launches for OneWeb, placing 428 satellites in orbit at a sustained rate of 34 to 36 satellites per launch. The complex deployment of these satellites was made possible by the Smart Dispenser, an intelligent dispenser developed and manufactured by Arianespace, as well as the prior installation of the satellites on the dispenser tiers in the production plant.
These satellites provide high-speed, low-latency services for a range of markets, including aeronautical, maritime and emergency response operations. The new-generation launcher Ariane 6 has the capacity to deploy satellites in low-Earth orbits, with a large payload capacity of up to 80 satellites.
-
Telecommunications: VA261 Intelsat 35, Heinrich Hertz and Syracuse 4B mission (GTO)

Telecommunications missions are essential to providing reliable, high-quality connectivity throughout the world. Placing a satellite in geostationary orbit enables us to cover a vast area of our planet.
Arianespace’s VA261 mission placed the German Heinrich Hertz satellite in orbit along with the French Syracuse 4B communications satellite, in a dual launch into geostationary transfer orbit (GTO). The VA261 mission represented a major challenge for Arianespace, demonstrating its expertise and ability to overcome significant obstacles such as satellite availability and possible postponements. Rigorous management of schedules and effective workforce mobilization were crucial to a successful launch. Every stage of the process, from satellite assembly to integration on the Ariane 5 launcher, including extensive testing to guarantee system reliability, was carried out with the utmost precision.
-
Science: VA256 James Webb mission (Separation trajectory)
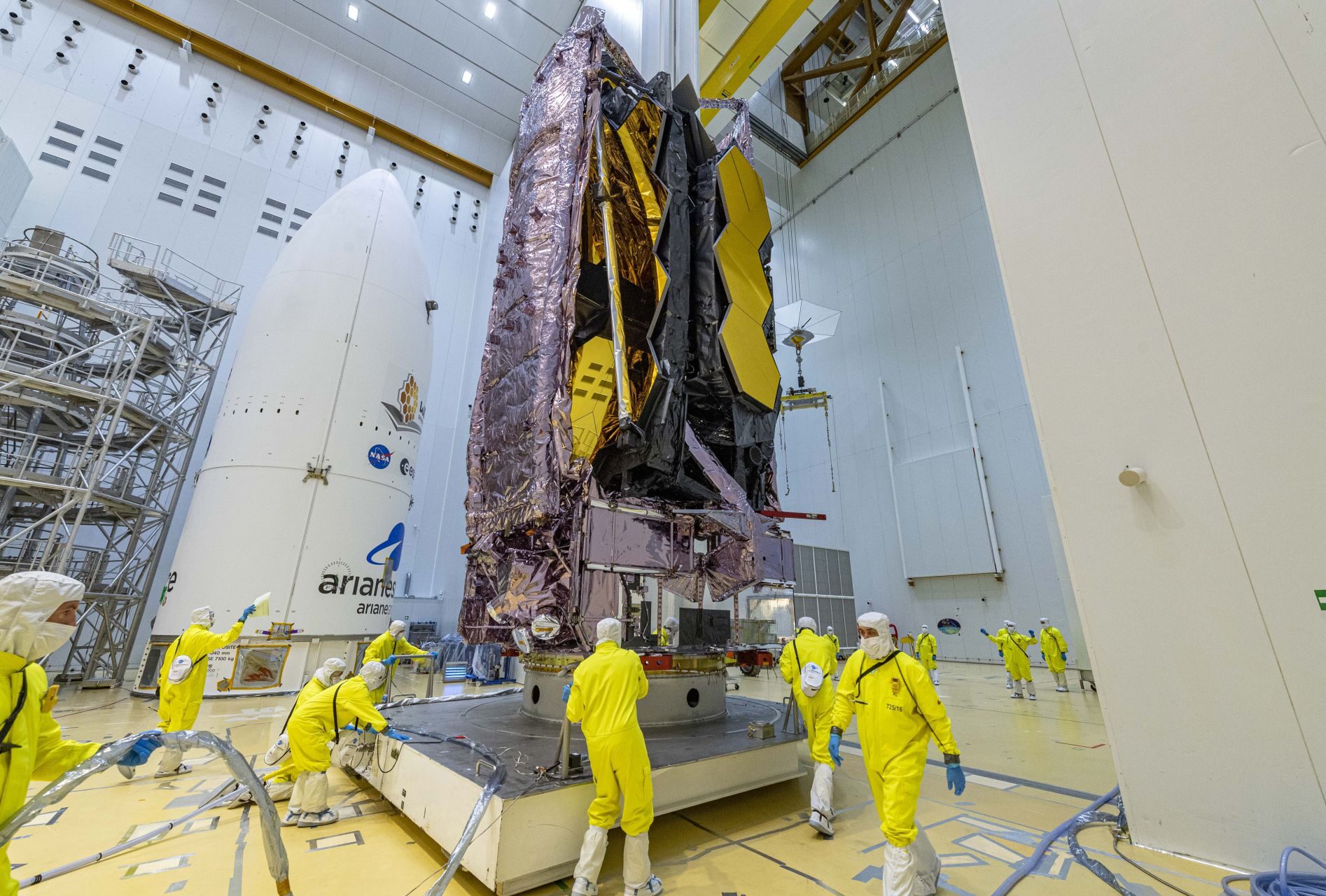

The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) represents a major international collaboration between NASA, ESA and CSA, with an investment of $10 billion and in excess of 20 years of development. The successor to the Hubble telescope, it offers optimized observation capabilities which set new standards in space exploration: improved spatial resolution, broad spectral coverage and advanced detection technologies. The launch of this project was entrusted to Arianespace and took place during the VA256 mission. The Ariane 5 launcher placed the JWST in a transfer orbit towards the Lagrange 2 point, 1.5 million kilometers from Earth.
The launch phase of the mission lasted 27 minutes and 11 seconds, marking the start of a 29-day journey to its final destination. During this journey, the telescope deployed its heat shield and assembled its primary mirror. Once in position, the JWST observes the universe, scrutinizing galaxies, planets and nebulae, and opening up new scientific perspectives. This mission is ESA’s 62nd and Arianespace’s 28th scientific mission, demonstrating the expertise of Arianespace in operating complex space missions.
-
Earth Observation: VV24 Sentinel mission (SSO)
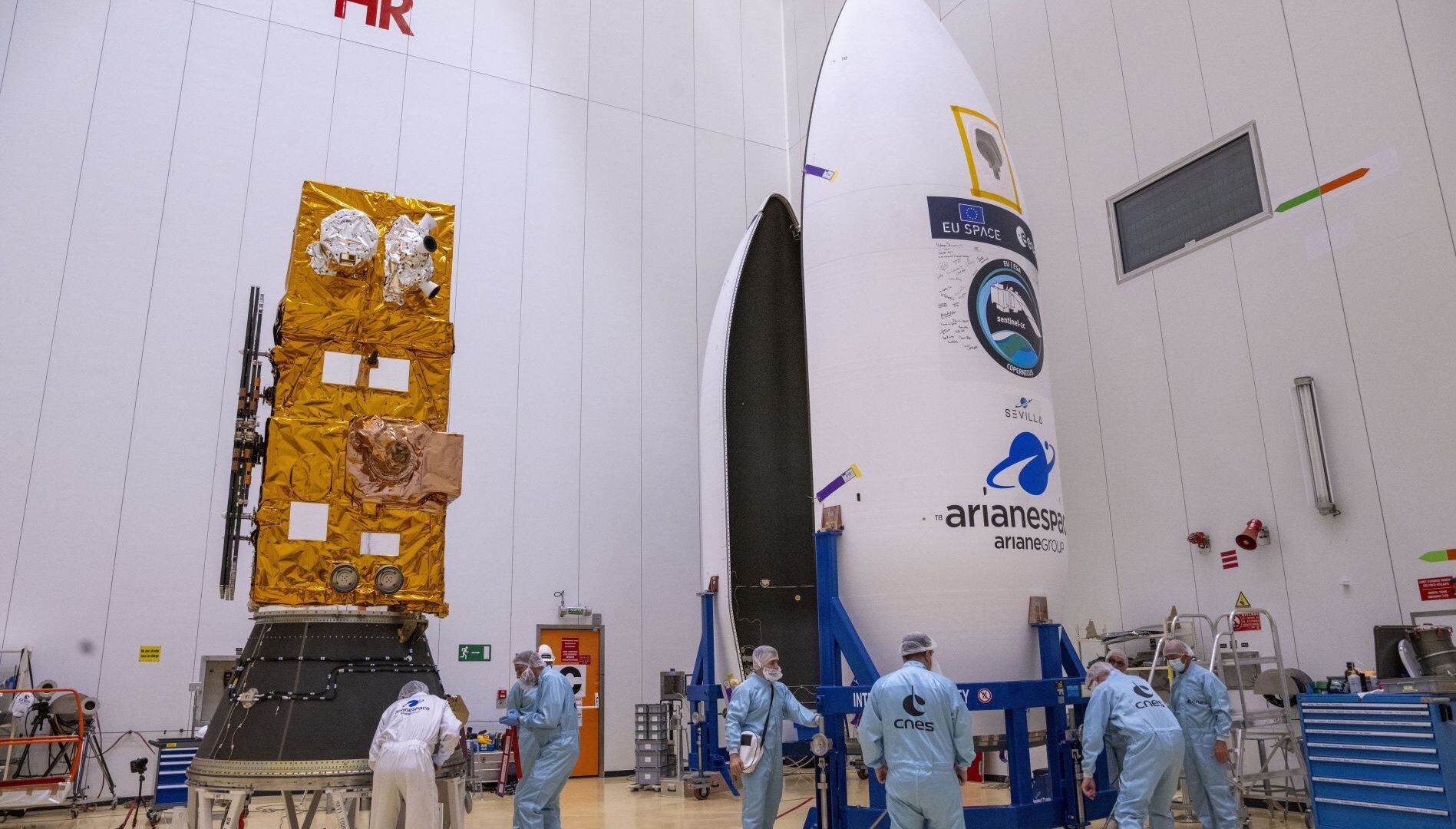

Earth observation missions, such as the Copernicus program developed by ESA in collaboration with the European Commission, illustrate Europe’s commitment to the climate. For example, the VV24 mission placed the Sentinel-2C satellite in orbit on board the Vega launcher, in sun-synchronous orbit at an altitude of 775 km. This satellite offers high-resolution multispectral imaging capabilities and is essential for natural resource management, agriculture and disaster response. The Vega and Vega C launchers, optimized for multiple deployments in low-Earth orbit, offer precision and flexibility to ensure the reliability of environmental monitoring and emergency management operations.
Arianespace orchestrated the VV24 mission with rigorous schedule management and effective mobilization of its specialist teams. The preparation and integration of the Sentinel-2C satellite on the Vega launcher were carried out at the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, requiring constant adjustments to adapt to climate conditions and to meet launch deadlines.
-
Navigation: VA244 Galileo mission (MEO)

The VA244 mission by Ariane 5 marked a major milestone in the deployment of the Galileo constellation. Four Galileo satellites designed by OHB System were placed in Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) at an altitude of 23,222 km, boosting satellite navigation services in Europe. Each satellite weighs 715 kg and offers extremely precise positioning, essential for advanced civil and security applications.
The mission mobilized Arianespace technical and logistics experts to ensure flawless preparation and integration of the satellites. This launch was the last in a series of three for Galileo using the ES version of Ariane 5 with a storable propellant upper stage. It highlighted the synergy between European entities such as ESA, the European Commission, OHB System and SSTL. This cooperation was decisive for the success of the mission and illustrates Europe’s ability to operate complex space projects.
Ariane 6: Ariane 6: the next-generation solution
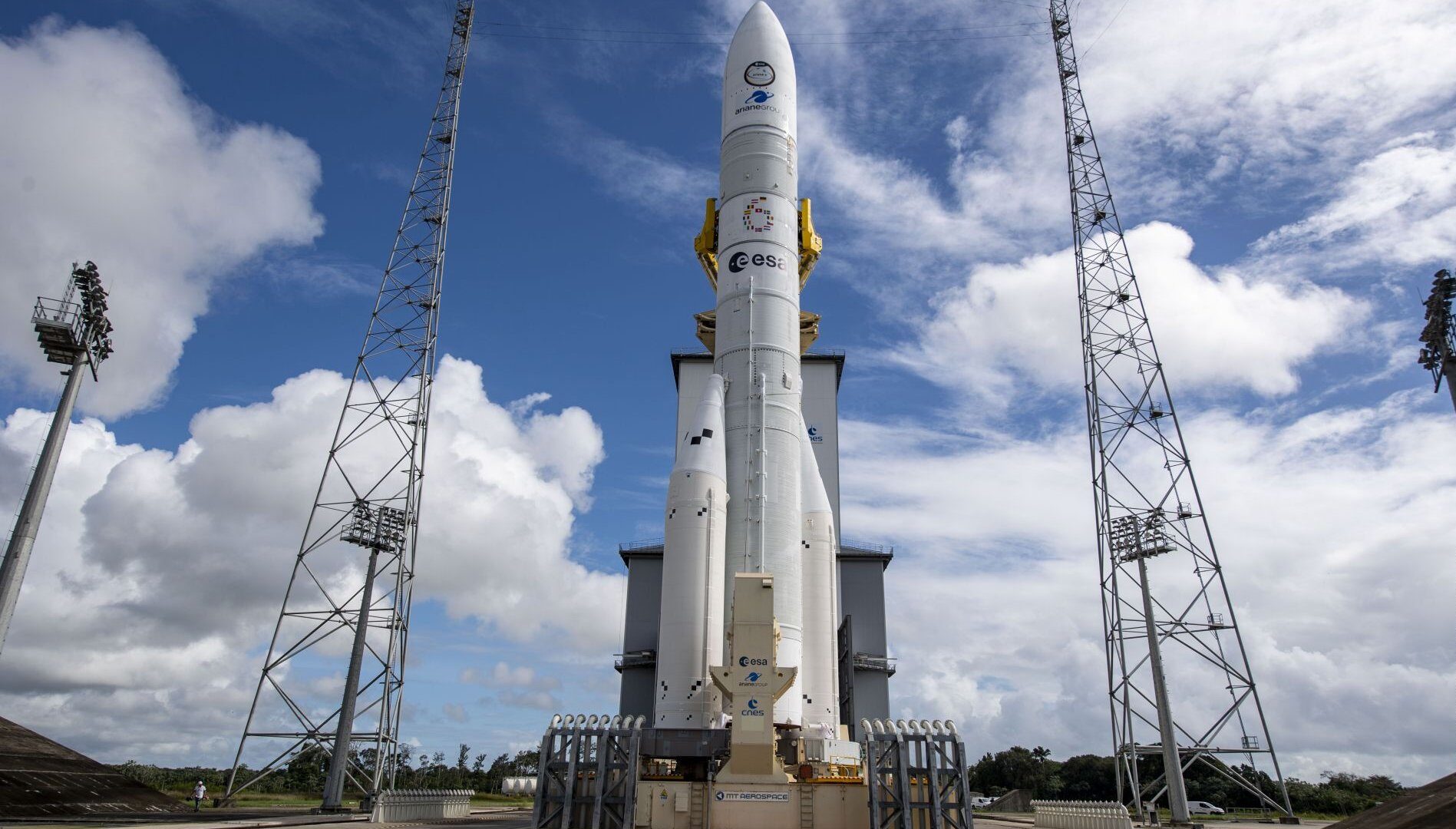

Ariane 6 is an innovative launch solution designed to offer the same level of precision and reliability as Ariane 5, yet with unrivalled performance, versatility and modularity. The two versions of the launcher, Ariane 62 (two boosters) and Ariane 64 (four boosters), mean it can perform a wide range of missions and launch all types of payloads, into all types of orbits. Ariane 6 provides extremely precise coverage of all Earth orbits and injections on specific trajectories, to meet commercial and institutional needs with optimum efficiency, while guaranteeing Europe autonomous access to space.
It is equipped with the Vinci engine, which can be re-ignited up to four times, and an auxiliary propulsion unit (APU). Ariane 6 offers exceptional flexibility for complex missions, such as deploying large constellations in several different orbital planes. The use of common components with Vega C reduces production and launch costs, making Ariane 6 a highly competitive launcher.